Money
Black Friday: The Holiday Surge in U.S. Consumer Debt and Spending
Black Friday
Visualizing the surge in U.S. consumer debt and spending
The Chart of the Week is a weekly Visual Capitalist feature on Fridays.
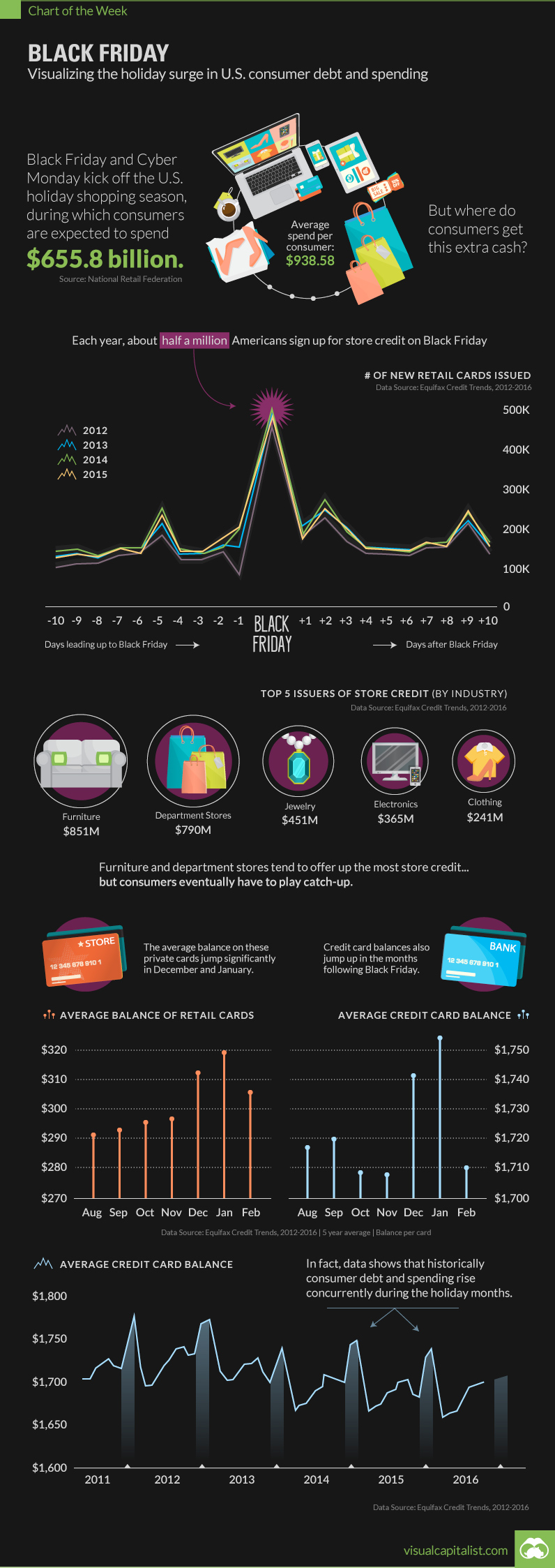
Next week, Black Friday and Cyber Monday will kick off the start to the U.S. holiday shopping season, during which consumers are expected to spend a total of $655.8 billion this year.
With the average bill coming in at $938.50 for holiday spending, where are people finding the extra cash?
We looked back at the last five years of Equifax data to see how consumer debt correlates to holiday purchases.
There’s Credit In Store
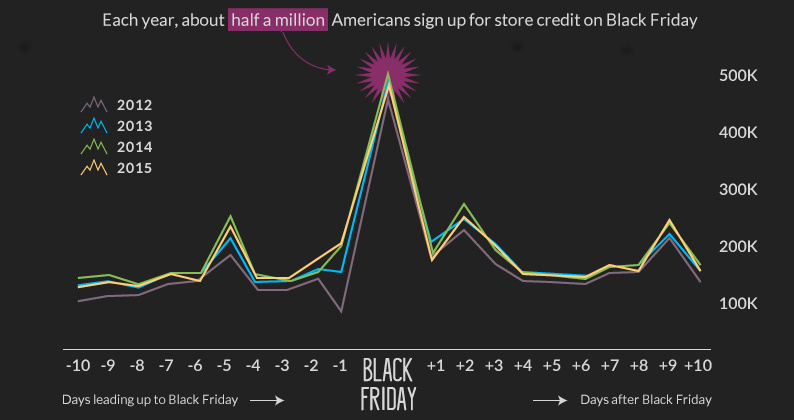
One way consumers take advantage of Black Friday deals is through the issuance of store credit. Specifically, Black Friday traditionally sees a noteworthy surge in signups to private label cards – the kind redeemed at stores like Macy’s.
Each year, roughly half a million Americans are signing up for new accounts on Black Friday:
| Private label cards issued | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prior 10 days (Avg.) | 130,312 | 153,605 | 164,341 | 162,006 |
| Black Friday | 463,292 | 485,512 | 502,805 | 491,873 |
| Following 10 days (Avg.) | 167,144 | 181,454 | 182,320 | 181,903 |
Furniture and department stores are among the biggest providers of this type of credit to consumers. Here are the five-year averages by industry for the months of November and December:
| New store credit issued (Nov/Dec) | $ millions |
|---|---|
| Furniture | 851 |
| Department stores | 790 |
| Jewelry | 451 |
| Electronics | 365 |
| Clothing | 241 |
Charge it, please
This bump in activity doesn’t stop with new signups for store credit. The average balances on store cards and credit cards both jump noticeably in the months following the holiday season:
| Month | Store Card Balance (5-Year Average) | Credit Card Balance (5-year Average) |
|---|---|---|
| August | $291 | $1,717 |
| September | $293 | $1,720 |
| October | $296 | $1,709 |
| November | $298 | $1,707 |
| December | $313 | $1,742 |
| January | $320 | $1,756 |
| February | $308 | $1,710 |
Every year is different, but the data always follows the same trend.
Stocking up on Black Friday deals is not cheap, and extra dollars spent eventually make their way onto the credit card statement with the cost of interest added on.
Money
How Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
See how much the debt-to-GDP ratios of advanced economies have grown (or shrank) since the year 2000.
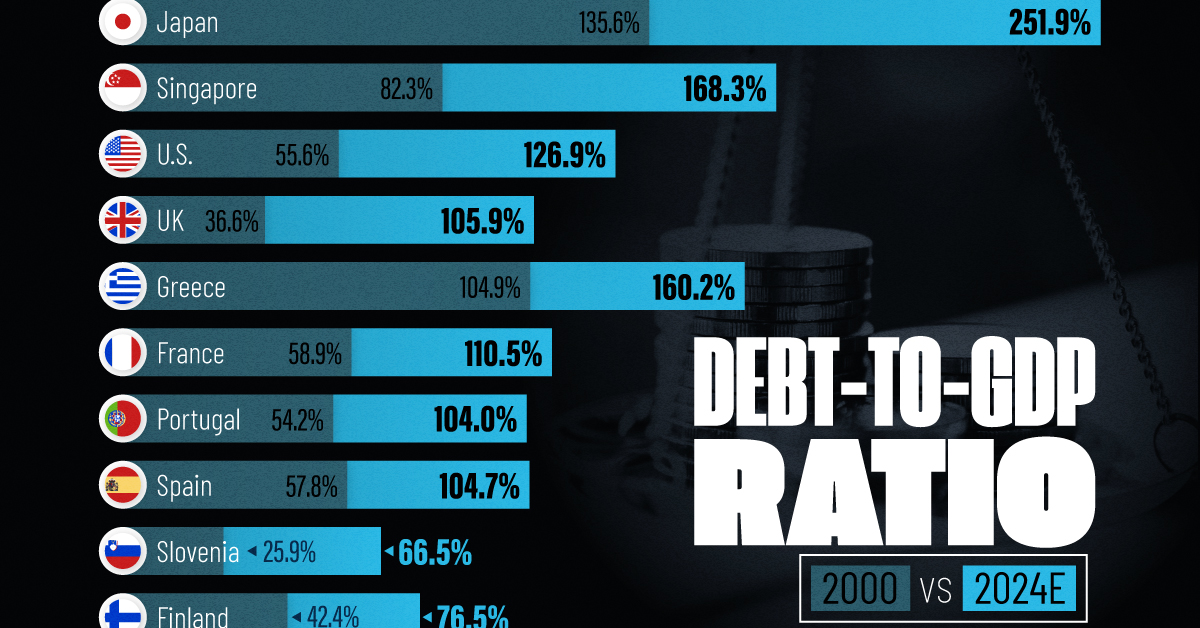
How Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
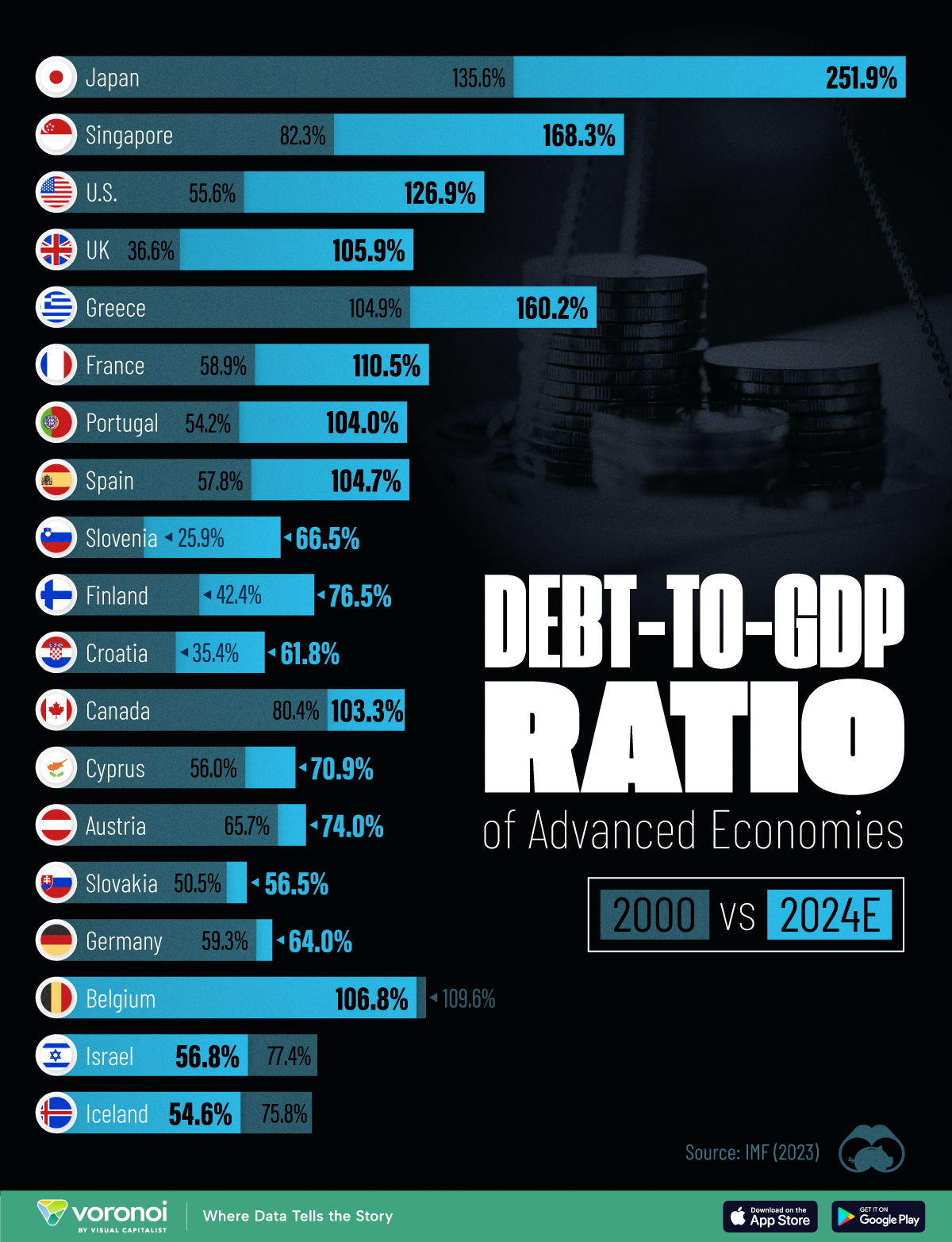
Government debt levels have grown in most parts of the world since the 2008 financial crisis, and even more so after the COVID-19 pandemic.
To gain perspective on this long-term trend, we’ve visualized the debt-to-GDP ratios of advanced economies, as of 2000 and 2024 (estimated). All figures were sourced from the IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Data and Highlights
The data we used to create this graphic is listed in the table below. “Government gross debt” consists of all liabilities that require payment(s) of interest and/or principal in the future.
| Country | 2000 (%) | 2024 (%) | Change (pp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 135.6 | 251.9 | +116.3 |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 82.3 | 168.3 | +86.0 |
| 🇺🇸 United States | 55.6 | 126.9 | +71.3 |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 36.6 | 105.9 | +69.3 |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 104.9 | 160.2 | +55.3 |
| 🇫🇷 France | 58.9 | 110.5 | +51.6 |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 54.2 | 104.0 | +49.8 |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 57.8 | 104.7 | +46.9 |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 25.9 | 66.5 | +40.6 |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 42.4 | 76.5 | +34.1 |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | 35.4 | 61.8 | +26.4 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 80.4 | 103.3 | +22.9 |
| 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 56.0 | 70.9 | +14.9 |
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 65.7 | 74.0 | +8.3 |
| 🇸🇰 Slovak Republic | 50.5 | 56.5 | +6.0 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 59.3 | 64.0 | +4.7 |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 109.6 | 106.8 | -2.8 |
| 🇮🇱 Israel | 77.4 | 56.8 | -20.6 |
| 🇮🇸 Iceland | 75.8 | 54.6 | -21.2 |
The debt-to-GDP ratio indicates how much a country owes compared to the size of its economy, reflecting its ability to manage and repay debts. Percentage point (pp) changes shown above indicate the increase or decrease of these ratios.
Countries with the Biggest Increases
Japan (+116 pp), Singapore (+86 pp), and the U.S. (+71 pp) have grown their debt as a percentage of GDP the most since the year 2000.
All three of these countries have stable, well-developed economies, so it’s unlikely that any of them will default on their growing debts. With that said, higher government debt leads to increased interest payments, which in turn can diminish available funds for future government budgets.
This is a rising issue in the U.S., where annual interest payments on the national debt have surpassed $1 trillion for the first time ever.
Only 3 Countries Saw Declines
Among this list of advanced economies, Belgium (-2.8 pp), Iceland (-21.2 pp), and Israel (-20.6 pp) were the only countries that decreased their debt-to-GDP ratio since the year 2000.
According to Fitch Ratings, Iceland’s debt ratio has decreased due to strong GDP growth and the use of its cash deposits to pay down upcoming maturities.
See More Debt Graphics from Visual Capitalist
Curious to see which countries have the most government debt in dollars? Check out this graphic that breaks down $97 trillion in debt as of 2023.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001